Project management has become essential for businesses to run smoothly, and conflict management is a crucial aspect of it.
Companies rely on project management systems to deliver their products/services efficiently, managing team workflow and timing to achieve goals.
Agile is a flexible and practical approach to software development that stands out among other project management methods. It excels in executing various tasks.
Traditional Project Management Overview
The traditional Project Management approach, also known as the waterfall method, follows a linear sequence where all phases of a process occur in order.
It relies on predictable tools and experience, with each project following a standard life cycle of feasibility, planning, design, building, testing, production, and support.
This approach requires full planning upfront, without flexibility for changing requirements. It considers time and cost as variables while assuming requirements are fixed, resulting in a rigid process that is unsuitable for large projects and disallows changes once development begins.
Benefits of traditional methodology
- Clearly defined objectives
- Ultimate control
- Clear documentation
- More accountability
Agile Project Management Overview
Agile management certification prioritizes teamwork, customer collaboration, and flexibility, unlike the traditional approach which focuses on upfront planning for cost, scope, and time.
Agile is an iterative process that emphasizes customer feedback and continuous releases throughout the software development project.
Agile software development is centered around adapting to change and teamwork to produce results, instead of following a strict process. Adaptive planning is a key aspect of Agile, making it popular among project managers worldwide.
Scrum and Kanban are two widely used Agile frameworks that prioritize decision-making and avoiding time consumption on variables that may change.
They prioritize customer satisfaction and use available teams to accelerate software development at each stage.
Benefits of Agile project management
- Flexible prioritization
- Early and predictable delivery
- Predictable costs and schedules
- Improves quality
- More transparency
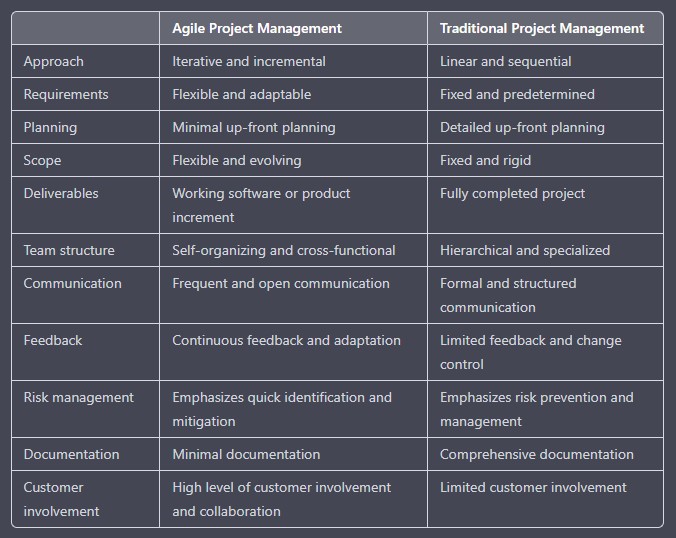
Difference between traditional and agile project methodology
The table down below shows the major differences between the traditional and agile project methodology.
| Characteristics | Agile approach | Traditional approach |
| Organizational structure | Iterative | Linear |
| Scale of projects | Small and medium scale | Large-scale |
| User requirements | Interactive input | Clearly defined before implementation |
| Involvement of clients | High | Low |
| Development model | Evolutionary delivery | Life cycle |
| Customer involvement | Customers are involved from the time work is being performed | Customers get involved early in the project but not once the execution has started |
| Escalation management | When problems occur, the entire team works together to resolve it | Escalation to managers when problem arise |
| Model preference | Agile model favors adaption | Traditional model favors anticipation |
| Product or process | Less focus on formal and directive processes | More serious about processes than the product |
| Test documentation | Tests are planned one sprint at a time | Comprehensive test planning |
| Effort estimation | Scrum master facilitates and the team does the estimation | Project manager provides estimates and gets approval from PO for the entire project |
| Reviews and approvals | Reviews are done after each iteration | Excessive reviews and approvals by leaders |
Why is Agile preferred not traditional PM approach
Many developers and project managers prefer to use the agile methodology for a variety of reasons. Some of them are discussed below:
1. More Flexible
The agile methodology is more flexible than the waterfall approach in adapting changes to the product or process.
The agile method allows for experimentation and deviation from the plan if team members see a need, putting the emphasis on the product instead of rigid structure.
Unlike the traditional linear, top-down approach, the agile method is not limited to a specific flow, allowing for last-minute changes to be incorporated without affecting the outcome or disrupting the project schedule.
2. More Transparency
The agile methodology is transparent, with clients and decision-makers actively participating in initiation, planning, review, and testing. In contrast, the traditional approach has the project manager in control, limiting the involvement of others in major decisions.
The agile methodology allows team members to monitor progress from start to finish, promoting a healthy work environment through its level of transparency.
3. Ownership and Accountability
The level of ownership and accountability in project management approaches can greatly differ.
Traditional PM puts the sole ownership with a designated project manager, while customers only have input during planning.
On the other hand, in agile methodology, all team members share ownership and actively contribute to completing sprints within time frames, with progress being visible throughout the project.
4. Constructive Feedback
Traditional project management follows a strict plan with set processes and defined deadlines, so significant changes or feedback are often disregarded. In contrast, the agile approach embraces constant feedback to improve outcomes.
This adaptability has made it a popular choice among project managers and software developers, as it allows for better responding to customer requests and delivering high-quality results within the established time frame.
5. Project Completion
Traditional project management is commonly used for simple projects due to its linear approach and aversion to changes. On the other hand, Agile is a better choice for managing large and complex projects with multiple interdependent stages.
How to choose the correct approach
There is no universal methodology that fits all projects or organizations. The choice of method depends on factors like project nature, size, resources, etc.
The final decision is usually made by the project manager in consultation with other project stakeholders at the beginning of the project.
Mentioned below are some factors you can take into consideration while choosing a suitable methodology for your project.
Project Requirements:
- If requirements are clear and stable, go with traditional PM.
- If requirements are unclear or prone to change, choose agile PM.
Technology:
- Traditional PM is suitable for projects without new technology or tools.
- Agile PM allows experimentation with latest technology.
Risks and Threats:
- Traditional PM may not be suitable for projects with high risks.
- Agile PM addresses risks sooner and is better for risk management.
Resources:
- Traditional PM works well for complex projects with large teams.
- Agile PM is suitable for projects with a limited number of experienced team members.
End Product Criticality:
- Traditional PM is suitable for critical products with heavy documentation.
- Agile PM may not be suitable for critical products with lesser focus on documentation.
