Dynamo: Definition, Functions, Components, Types, Working Principles
In general, a dynamo is a device useful for generating electrical energy, from which it was initially in the form of mechanical energy. The use of dynamo in electronic circuits themselves is pretty widespread. One of them is used in power generators, for example, as found in hydropower or PLTU.
The following article will thoroughly discuss the function of the dynamo, its components, types, and how the tool works. Take advantage of the complete information below.
What Is a Dynamo? A Definition and Explanation
Dynamo is a tool that functions to convert mechanical energy into electrical energy. To convert mechanical energy into electricity, this dynamo will utilize the electromagnetic working principle from the coil and the magnetic field it has.
By rotating the coil in a magnetic field or vice versa, the electronic device will produce induction and an electromotive force (EMF). When a lock with a wave of wire is rotated or moved, a magnetic field will arise, and a voltage will be created in the ring. Then, the generated electrical energy will be used to rotate the dynamo.
The use of dynamos is also very diverse and is used for various types of electronic equipment, such as fans, blenders, and electric drills. It covers the application of household-scale electronic equipment, and dynamos are also part of the power generation equipment in hydropower plants, steam power plants, and so on.
What Are the Main Components of a Dynamo? A Detailed Explanation
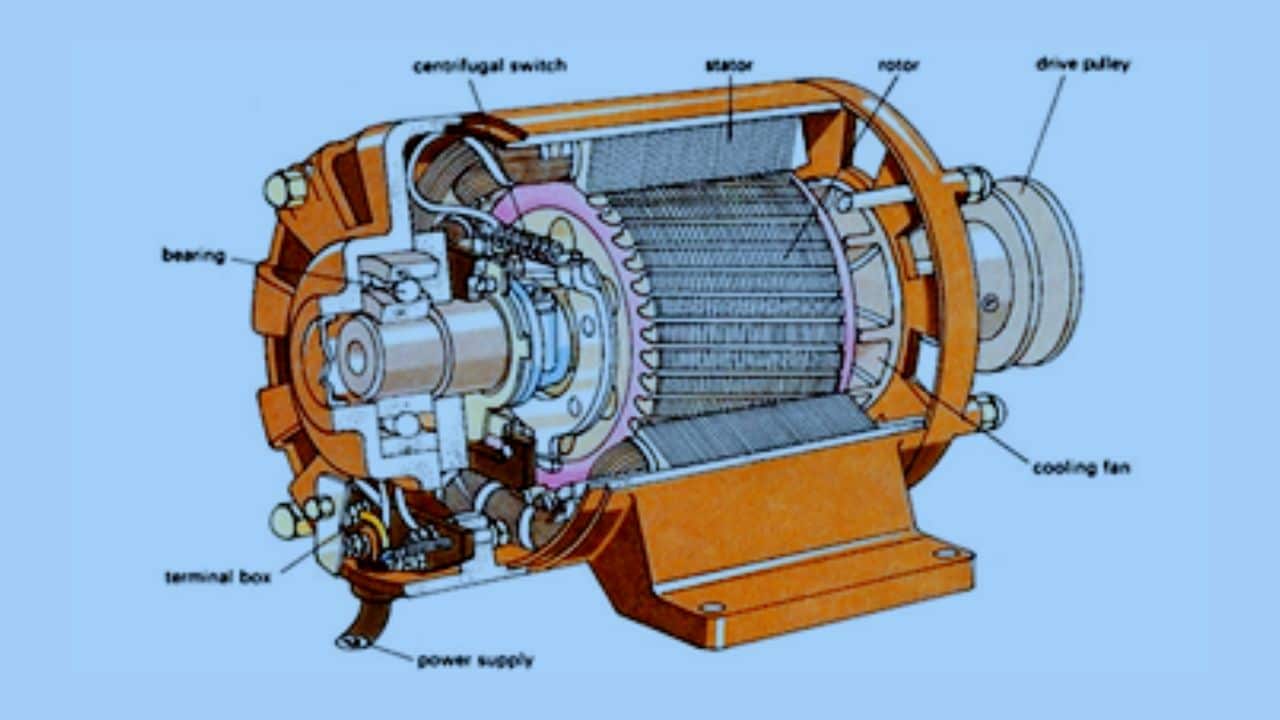
Dynamo is also known as a dynamic electric machine. To be able to work, the tool is also supported by various components that compose it. Then what are the parts of the dynamo?
The dynamo parts are :
- Rotor.
- stator.
- brushes.
- Bearings.
- Main Shaft.
- Motor Housings.
- Drive Pulleys.
Check out the full review of each part of the dynamo below!
1. Rotors
The rotor is a dynamo component that is wrapped around a copper wire. The rotor is the part whose job is to move and generate rotation. In the rotor, there is a shaft that functions to help as the output of the driving force.
The rotor also has components consisting of wire coils and functions to assist the movement of the tool. The wire coil in the rotor significantly influences the speed that the dynamo will generate.
When there are more wire turns, the rotor will move faster. Likewise, if the number of rotor turns is small, the rotor rotation will weaken.
2. Stators
If the rotor is a moving component, the stator is stationary. The rotor is a static part with a wire wound in it. Which wire coil contained in the stator functions to produce a magnetic field? And this magnetic field will be located around the rotor later.
The more turns of wire used, the greater the magnetic field generated, and vice versa.
3. Brushes
Furthermore, the dynamo also has a component called a brush. The brush part is often referred to as a brush, and the material is made of copper wire. Brushes are usually placed at the end of the rotor. Its function itself is to connect the electric current with the rotor.
When the rotor moves, the brush will experience friction. Then the friction that arises will gradually connect the electric current to generate an electric current.
4. Bearings
Bearings are also known as bearings. The bearing is located between the bearings between the shaft and also the motor housing. Bearings are usually made of materials that have low friction.
This component helps maintain the rotation of the dynamo to avoid obstacles.
5. Main Shaft
Furthermore, there is also a component called the main shaft. The main shaft is an object that functions as an axis or axis. This axis helps lay various other supporting equipment.
For example, in a fan, the propeller must be connected to the dynamo shaft to rotate, likewise, with other electrical tools.
The shaft or main shaft will be connected and become the foundation of various equipment; therefore, the main post is usually made with materials that do not rust easily. As well as withstand high rotation and temperature changes.
6. Motor Housings
The motor housing is fragile, made of metal, and functions as the outer protection of the dynamo components.
Aside from being a protector, the motor housing also minimizes the dangers the motor poses. By preventing the rotation of the axis is not too high.
7. Drive Pulleys
With a dynamo’s help, the pulley moves the rotation contained in the motor and transfers it to other components.
For example, in a fan, the pulley moves the dynamo’s rotation. You can go to other components in the fan.
From Mechanical Energy to Electrical Power: The Working Principle of Dynamos
To understand more about what a dynamo means, let’s look at the specifics of how a dynamo works first.
The working principle of the dynamo is as follows:
- To be able to work, the dynamo utilizes a rotating magnetic field contained in a coil. The coil contained in the doer has a magnetic field of positive and negative poles.
- Then, when the coil experiences movement, the two poles will act and induce each other to produce an alternating current. When the magnetic field contained in the coil rotates, it will trigger an electromotive force that has alternating current (AC).
- To be able to convert AC into DC. Then you have to replace the ring on the dynamo with the commutator. The ring on the dynamo helps produce the desired type of current. The component must be fitted with a split ring (commutator) to make a direct current.
- Meanwhile, if you want to produce an alternating current, the split ring must be replaced with a double ring type.
Types of Dynamo Based on Current
Based on the type of current it generates, the dynamo is divided into two types. Both are AC dynamo and DC dynamo. The following is a complete discussion of the two kinds of dynamos.
1. Dynamo AC
The first type is the AC dynamo. This type is a dynamo that produces alternating currents.
On the AC dynamo, there are two rings connected to the brush. The two rings attached to the brush rotate 360° to the two magnetic poles in the coil.
As a result, the resulting magnetic induction will have an electromotive force in two different directions so that the resulting current is a type of alternating current (AC).
2. DC Dynamo
The next type of dynamo is the DC dynamo. Unlike the AC type, the DC dynamo only has one ring. The split ring contained in the tool is also known as the commutator. Where the commutator is included in the device will affect the resulting induced current.
With the commutator, the resulting induced current captures only 180° rotation of the rotor. The dynamo output will only produce DC (direct current).
Conclusion
A dynamo is a device that converts mechanical energy into electrical energy. The dynamo generates electrical power from a rotating coil in a magnetic field.
To produce electrical energy, the dynamo utilizes the electromagnetic phenomenon between the coil and the magnetic field to produce electricity from the induction process.
Because of its working principle, the dynamo is used for various purposes. Among them are used for players in electronic devices such as fans, mixers, and electric drills, for power plants such as hydropower, and so on.
That’s the whole discussion about dynamos. Hopefully, it’s helpful and easy to understand.
