In the internet world, many things can make network management more effortless. One of them is DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol). This protocol usually resides in a DHCP server device and automatically recognizes devices connected to a network.
Well, what is DHCP, and how does it work?
We will discuss DHCP in depth in this article. Starting from the meaning, function to the way it works. Let’s see the full explanation below!
What is DHCP?
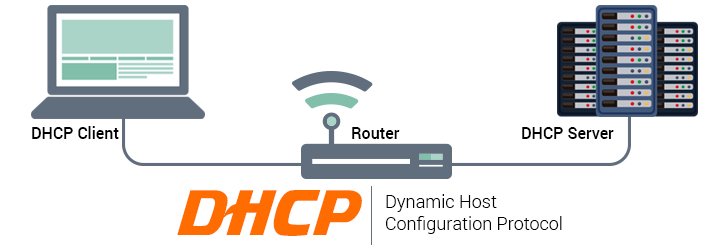
DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) facilitates the automatic propagation of IP addresses (internet protocol) to other devices.
Without it, the configuration must be done manually on each computer to get a different IP address. This will undoubtedly be inconvenient and time-consuming, won’t it? Especially if the configuration is done on an extensive network.
The IP Address or IP address itself is a string of numbers on a device that allows your device to connect to the Internet. So you can access web pages, emails, and more.
By using DHCP, IP addresses can be automatically shared to many devices simultaneously. That is why this device is widely applied to small and large networks.
Differences between DHCP Server and DHCP Client
In a computer network, there are the terms server and client. A server is a device that stores all data, manages, and regulates all activities on the web. At the same time, the client is a device that requests services from the server.
In DHCP, the terms DHCP server and DHCP client are also known. Then what is the difference between the two?
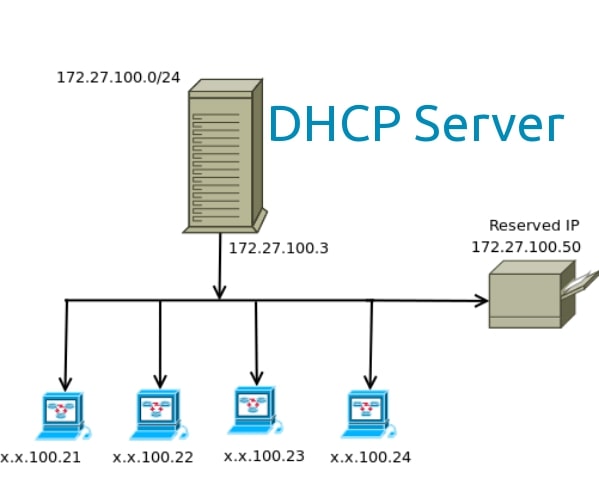
DHCP server is a device tasked to configure and assign IP addresses to existing client computers automatically. Meanwhile, other computers /devices, such as mobile phones, that receive IP addresses from DHCP servers are called DHCP clients.
DHCP servers typically assign a custom, dynamic IP address to each client computer. So, the IP address the DHCP server sends can expire at a specified time.
However, usually, the DHCP server will update the duration of the IP address automatically. This is where the advantage of using this tool so that even the client computer or sysadmin does not have to do anything.
DHCP Server function
Here are some DHCP server functions you need to know:
1. Manage and Distribute IP Addresses
In general, the function of this device is to manage and facilitate the distribution of IP addresses to client computers. This distribution process can be done to many devices at once automatically. This means you don’t need to configure it on every computer.
2. Prevent IP Conflict
IP conflict occurs due to two devices that have the same IP address. If this happens, the device cannot connect to the network.
By using this tool, errors in IP address sharing can be minimized. In addition, it can also manage the sharing of IP addresses well so that the possibility of errors is minimal.
3. Update IP Address Automatically
The IP address the server provides usually has an expiration or an expiration time. If the IP address is still in use but has expired, you will need to update or request a new IP address.
The Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol allows IP addresses to be updated automatically without reconfiguring.
4. Supports IP Address Reuse
IP addresses that have been used can be reused by client computers. However, to reuse, you must ensure another computer is not using the IP address.
The Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol server will help you check if the IP address is off and accessible so that the IP address can be used again.
How DHCP Server Works
When a user turns on a computer and connects it to a server with this service, the computer will automatically request an IP address for the server. Then the server answers the request until, finally, the laptop gets the IP address and connects to the network.
To learn more about how it works, please look at this service’s processes.
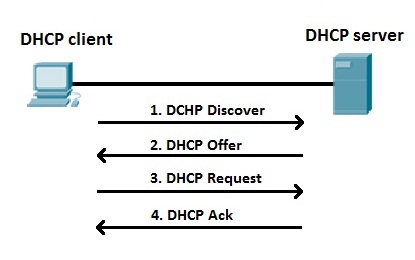
1. IP Least Discovery
The first stage is referred to as the discovery stage. When the client is connected to the network, the client will look for DHCP servers working on that network. The client will send a DHCPDISCOVER message to the network subnet using the destination address 255.255.255.255. Once found, the client will request the IP address on the DHCP server.
2. IP Least Offer
When the DHCP server receives a DHCPDISCOVER message from the client, the server will make an offer to it by sending a DHCPOFFER message to the client. The message contains the client id, the IP address offered, the subnet mask, the duration of use, and the IP address of the DHCP server.
3. IP Lease Request
After receiving the offer from the DHCP server, the client then approves the proposal provided by providing a DHCPREQUEST message to the server. The content of the message is to request that the server lend one of the IP addresses available in the DHCP set of IP addresses.
4. IP Lease Acknowledge
At this last stage, after the server receives a request message from the client. The server will send a message in the form of a DHCPACK packet to the client. This package contains the IP address, rental duration, and other configuration information the client may need.
At the IP address provided stage, the IP configuration process is complete. Once the IP address is given to the client, the server will cross out and mark the IP address in their database.
Once this process is complete and successful, the client computer can use the network and exchange data with other client computers on the local network.
Conclusion
DHCP is a service that distributes IP addresses to client computers automatically. With this tool, a server admin does not need to set the IP address on each client computer that wants to connect to the network.
In addition, IP Conflict can be prevented with DHCP servers because it has flagged the IP address used in the DHCP pool. IP addresses used and in the off-state can be used again (reusable). That is why many parties implement this service on their network.
Such is the review of DHCP for networking. Hopefully useful