In the following we will explain about what is the function of the PCI Express Slot on the Motherboard in full so it is hoped that it will provide a deep understanding for you.
PCI Express Slot Function
Peripheral Component Interconnect Express, better known as PCI Express (and abbreviated as PCIe or PCI-E) and has become a standard on modern motherboards as interfaces with computer expansion cards.
PCI-E is used as a connection device to the motherboard and also as an expansion card interface.
The new standard for personal computers is called PCIe 3.0 which is an improvement over its predecessor by using a new topology that allows faster data transfers.
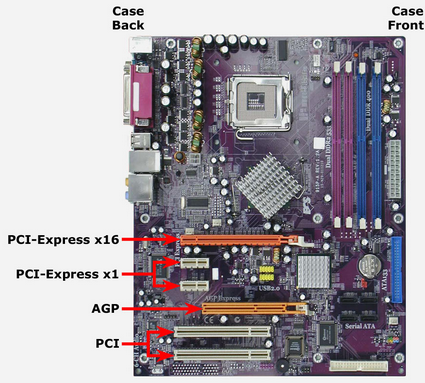
The new PCI-E 3.0 technology differs from the previous PCI, PCI-X and AGP boards in many ways, including:
- Communications consist of data traffic and status messages that are packaged and depacketed .
- Data is sent via paired point-to-point serial links, called paths, allowing data to be moved in both directions simultaneously and allowing more than one pair of devices to communicate simultaneously.
- PCI-E slots are available from one to 32 lanes with a power of 2 (1, 2,4, 8 etc.). Each “line” is a pair of data transfer lines, one for transmission and one for receiving, and consists of 4 cables. The number of lanes in the slot is denoted by the previous x, i.e. x16 designates a 16 lane PCI-E card.
- Higher bandwidth is provided by channel grouping – using multiple paths for a single device.
- Serial bus transmits data faster than parallel buses due to the limitation that the latter requires data to arrive simultaneously at its destination (This relates to the frequency and wavelength of a single bit). With serial buses there is no requirement for signals to come simultaneously.
- PCI-E follows a layered protocol consisting of 3 layers: transaction layer, data link layer, and physical layer.
The following are the transmission rates and bandwidth for the various PCI-E buses. This rate is for total transmission in both directions, 50% is in both directions:
- PCI Express 1x 500 MB / s
- PCI Express 2 × 1000 MB / s
- PCI Express 4x 2000 MB / s
- PCI Express 8x 4000 MB / s
- PCI Express 16x 8000 MB / s (x16 card is the largest commonly used size.)
- PCI Express 32 × 16000 MB / s
In comparison, a PCI card has a bandwidth of 132 MB / s; AGP 8x: 2,100 MB / s; USB 2.0: 60MB / s; IDE: 100 to 133 MB / s; SATA: 150 MB / s; SATA II: 300 MB / s; Gigabit Ethernet: 125 MB / s; and Firewire 800: approx. 100 MB / s.
Hopefully our explanation of what is the function of the PCI Express slot on this motherboard will be able to help you get to know and explore the topics we discussed in this article. PCI Express Slot Explained
