Desktop and laptop computers (or other types of computers) have this kind of storage media. The storage media is the primary storage media (primary) and secondary storage media.
RAM ( Random Access Memory ) is one of the main types of storage media in a computer, where data can be accessed randomly ( randomly ) regardless of the location of the data. RAM is volatile and can only store data if it has electrical power.

The amount of data that can be accommodated in RAM depends on the RAM capacity. RAM, which has a capacity of 8 GB, can undoubtedly store more data than RAM, with a total of only 2 GB or 4 GB.
Therefore, a large RAM capacity is one of the factors for optimal computer performance. Because to run various application programs, sufficient RAM capacity is needed so that a lot of data can be stored.
Types, How It Works, and Components in the RAM Module
Table of contents
- RAM functions on the computer
- How RAM works
- RAM component
- Difference between DIMM and SO-DIMM memory
- RAM type
- Memory timings
RAM functions on the computer
RAM is a temporary storage container for data that the CPU will process before being displayed in the form of information that the user can recognize. RAM is also an intermediary between the CPU and the boot or secondary storage media.
Secondary storage media such as hard disks, flash drives, or CD / DVDs have limited data access speeds. If the processor has to access files, process, and store data on these storage devices directly, the computer system will run very slowly.
Some of the other RAM functions include
Supports multitasking
Multitasking is a system state that can run more than one application simultaneously. When multitasking, RAM will be filled with a lot of application program data processed by the CPU.
To be able to multitask comfortably, you must use a large capacity of RAM to accommodate more data for running applications.
As an alternative to IGP VRAM
Modern processors are now equipped with IGP (Integrated Graphic Processor) as an easy (and inexpensive) display component solution. That way, PC users no longer need to buy a separate graphics card / discrete GPU, which costs much more.
To run correctly, IGP also requires VRAM. However, the CPU’s built-in IGP is not accompanied by VRAM due to space constraints. So, IGP will take advantage of part of the main memory capacity (RAM) as VRAM.
If you decide to use IGP on the CPU, you must use a large-capacity RAM to accommodate the system requirements and IGP VRAM allocation. You should also use high-speed RAM to increase IGP performance.
How RAM works in a computer
When a user wants to run an application program, the data or files needed to run the program will be taken from the secondary storage media (Hard disk / SSD). Then, the system transfers the data to RAM for further processing by the processor. After processing, the processor will display the results to the output device or return them to the storage device.
If the amount of data to be accommodated exceeds the RAM capacity, the operating system will perform a swap or “temporary move” procedure. The data will be temporarily moved to a space in secondary storage called a swap file or virtual memory.
Generally, data moved to virtual memory is active program data with low priority, such as applications or services running in the background. The swap process can cause computer performance to be not optimal, so the system runs slowly. To prevent this problem, use RAM with a capacity according to the specifications required by the operating system or application program that is running.
DIMM vs. SO-DIMM
DIMM, or Dual In-line Memory Module, is a RAM module used for modern desktop computers, such as PCs, workstations, or servers. The RAM DIMM memory has separate connector pins on each side of the module. All types of DDR RAM have a different number of connector pins and notch positions. The goal is that users do not install RAM on the computer because DDR memory is incompatible.
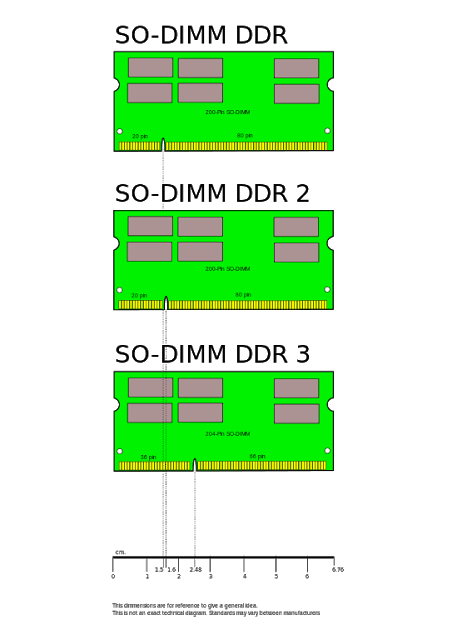
DIMMs are similar to SO-DIMMs, or Small Outline DIMMs, and are memory modules used for small computer devices such as laptops, notebooks, tablets, or on Mini-ITX size motherboards. Because it is intended for mobile devices, SO-DIMMs are usually half the size of DIMMs. The number of connector pins is also less than in the DIMM version.
Memory type DDR RAM
Currently, the RAM in circulation is generally DDR SDRAM ( Double Data Rate Synchronous Dynamic RAM). In the past, there were several types of RAM, such as DRAM ( Dynamic RAM), FP RAM ( Fast Page RAM), EDO RAM ( Extended Data Out RAM), and SDR RAM ( Single Data Rate RAM). Usually, the older the RAM type, the more expensive the price because the number of items is scarce and no longer produced.
DDR SDRAM can access two instructions at the same time so that it can transfer more data by using one frequency band in full. If the SDRAM memory can only process instructions on positive or negative waves, then DDR SDRAM can process instructions on positive or negative waves. Several types of DDR SDRAM memory include
DDR SDRAM (DDR1)
It is an early version of DDR RAM in modern computers. DDR SDRAM memory has a transfer rate of up to 400 MT / s with a maximum frequency of 200 MHz. Each DDR DIMM module has 184 pins; a 200-pin SO-DIMM requires 2.5 V.
| Name | Label | Frequency (MHz) | Effective Speed (MHz) | Bandwidth (MB/s) |
| DDR-200 | PC-1600 | 100 | 200 | 1600 |
| DDR-266 | PC-2133 | 133 | 266 | 2133 |
| DDR-333 | PC-2666 | 166 | 333 | 2666 |
| DDR-400 | PC-3200 | 200 | 400 | 3200 |
DDR2 SDRAM
To adjust the performance speed of the processor and graphics interface, memory manufacturers then present DDR2 RAM. The striking difference between DDR and DDR2 is an increase in data transfer speed, increased bandwidth, and a twofold increase in latency.
This change aims to produce optimal performance on computer systems. In addition, DDR2 voltage requirements are more efficient. If DDR memory requires a voltage of 2.5 volts, it differs from DDR2 memory which only requires a power of 1.8 volts.
DDR2 RAM is not compatible with previous DDR memory. This is because the DDR2 RAM module has a different notch position from the DDR memory module. If the DDR memory module only has 184 pins, the DDR2 DIMM RAM has 240 and DDR2 SO-DIMM 200 pins. Therefore, DDR2 memory cannot be installed in a DDR memory slot.
| Name | Label | Frequency (MHz) | Effective Speed (MHz) | Bandwidth (MB/s) |
| DDR2-533 | PC2-4266 | 266 | 533 | 4266 |
| DDR2-667 | PC2-5333 | 333 | 667 | 5333 |
| DDR2-800 | PC2-6400 | 400 | 800 | 6400 |
| DDR2-1066 | PC2-8500 | 533 | 1066 | 8500 |
DDR3 SDRAM
This type of DDR RAM only consumes 1.5 V of power, which is more efficient when compared to DDR2 1.8v or DDR 2.5v. DDR3 memory already uses 90 nm fabrication technology, so besides being more energy efficient, it also has a high density and increases data transfer speeds much faster than DDR2.
One DDR3 RAM module can have a capacity of up to 16 GB. Although both have 240 pins, DDR3 and DDR2 are incompatible due to differences in notches, power, and frequency speeds. For DDR3, SO-DIMM has 204 pins.
| Name | Label | Frequency (MHz) | Effective Speed (MHz) | Bandwidth (MB/s) |
| DDR3-1066 | PC3-8500 | 533 | 1066 | 8500 |
| DDR3-1333 | PC3-10600 | 667 | 1333 | 10600 |
| DDR3-1600 | PC3-12800 | 800 | 1600 | 12800 |
| DDR3-1866 | PC3-15000 | 933 | 1866 | 15000 |
| DDR3-2133 | PC3-17000 | 1066 | 2133 | 17000 |
DDR4 SDRAM
DDR4 RAM modules are produced using 30 nm fabrication technology to have a higher density, are more power efficient, and increase data transfer speeds much faster than DDR3. Theoretically, one DDR4 RAM module can have a capacity of up to 512 GB capacity.
However, a maximum DDR4 capacity of only 32 GB is often encountered. The power required for DDR4 memory is also only 1.2 V using 288-pin DIMMs and 260-pin SO-DIMMs.
| Name | Label | Frequency (MHz) | Effective Speed (MHz) | Bandwidth (MB/s) |
| DDR4-2133 | PC4-17000 | 1066 | 2133 | 17000 |
| DDR4-2400 | PC4-19200 | 1200 | 2400 | 19200 |
| DDR4-2666 | PC4-21330 | 1333 | 2666 | 21330 |
| DDR4-2933 | PC4-24000 | 1466 | 2933/3000 | 24000 |
| DDR4-3200 | PC4-25600 | 1599 | 3199/3200 | 25600 |
The RAM speed above is a standard specification commonly found on the market. Some RAM products, especially premium or high-end class, have specifications that exceed the standard with the XMP feature.
Components on the RAM module
- The SPD ( serial presence detect ) chip is a chip that contains the memory setting profile and standard specifications of the RAM module. SPD is usually detected automatically by the motherboard or BIOS, which aims to determine the RAM operation process. Some RAM manufacturers complete the SPD configuration with the XMP ( Extreme Memory Profile ) feature. With the XMP feature, RAM can be adjusted optimally, even more than the standard configuration, to produce faster performance. The XMP feature is usually included in premium or high-end RAM.
- RAM chip. The chip stores data before the CPU processes it. RAM chips are placed in a row on one side of the module ( single side aka single-rank ) or both sides of the module ( double side aka double-rank ) in RAM. The number of ranks will determine the number of RAM chips installed.

- The heatsink or heat spreader is metal finned to conduct heat generated by the RAM chip. The heatsink covers the RAM chip to protect it from overheating, which can physically damage the chip. Heatsink is usually used for premium or high-end RAM.
- The notch is a small hole where the latch locks the module in the memory slot on the motherboard. Incisions are located on the sides and bottom of the memory module connector. The notch on the connector prevents the memory module from being placed in a slot that does not match the RAM type. The kind of memory that a computer system can use is a memory that has a notch that fits the memory slot on the motherboard.
- RAM connector that attaches to the memory slot on the motherboard. Shaped like a copper-yellow pin on the bottom of both sides of the memory module. This memory connector is quite sensitive to debris that can cause system errors. If the connector is dirty, we can clean the connector by rubbing a rubber wiper.
- < UNK> Some RAM modules, especially those intended for the premium class, are usually equipped with RGB LEDs. This is designed as an additional aesthetic feature on the computer system through colored lights. The color can be changed according to the wishes of the computer user.
RAM timing
In general, RAM performance is determined based on its transfer speed. The data transfer rate of a RAM is usually known from the clock speed or frequency speed multiplied by 16. For example, DDR3-1600, with a frequency of 800 MHz, has a transfer rate of 12800 MT / s.

Apart from the clock speed, the timing factor affects the performance of RAM. Timing in RAM (usually listed on the module specification label) represents complex processes in RAM while working.
The timing is divided into four numbers written sequentially: CL, TRCD, TRP, and TRAS. Sometimes some RAM also lists a fifth number, the command rate (usually reported as 1T).
Examples of timings in RAM are, for instance, 7-8-8-24. Think of RAM as a table with columns and rows containing space to store various data.
- CL or CAS Latency is the time it takes for RAM to respond to commands from the processor. The smaller the CL value, the better the RAM performance. CL is the most crucial number on RAM performance compared to other numbers on memory timings.
- TRCD or ” RAS to CAS delay ” is the time for RAM to activate between rows and columns during data processing. The smaller the TRCD value, the faster activation before processing data in RAM.
- TRP or ” RAS precharge ” is the time for RAM to move to the next row. The smaller the value, the faster the performance of a RAM
- tRAS or ” active to precharge delay ” is the time RAM waits for the next instruction to enter after finishing the previous education. The tRAS value is at least the sum of the three previous timing values (because it is the last process after going through the previous three processes) with a tolerance of several clock cycles. As in the last example, timing: 7 + 8 + 8 = 23. The TRAS value is 23 + 1 = 24. Adding the value of 1 is for stability. Because if the weight on timing exceeds the limit of RAM capacity. As a result, data processing can be interrupted, leading to system errors.
Command Rate (CMD) is the time it takes for the first time the RAM is active. By default, CMD is usually set at 1T, the fastest lag time. Like other values, the smaller the CMD number, the better the RAM performance.
That briefly explains the function, how it works, and the technical specifications of RAM on a PC. It may be helpful to…