RAM (random access memory) is an essential component in any gaming PC. Adding more RAM can increase the responsiveness of the system and increase the frame rate when compared to a system with less memory.
Read about how RAM works, how to find compatible modules, and how much memory you need for gaming. This is guide How to Choose RAM for Gaming PC .
How RAM Works?
The function of RAM is to store short-term data that the PC needs to operate properly. But unlike hard disk drives or solid-state drives (SSDs), which store data indefinitely, RAM resets every time the system reboots.
RAM is “volatile memory”, meaning it only stores data when it has power, as opposed to a “non-volatile” HDD or SSD. Programs are temporarily loaded into RAM when in use, but remain on the storage drive permanently (until they are deleted).
Computers need instant access to temporary data to run programs and carry out tasks. Modern gaming PCs, for example, need to pick up artwork assets quickly. Games read and write data to RAM because they are faster than accessing data to storage devices.
What RAM is Compatible with Your Motherboard?
Before you start thinking about RAM capacity and frequency, you should make sure that the RAM is compatible with your motherboard and processor. The wrong type of module will not work, while RAM with the wrong specifications for your system can degrade performance.
Module Type
RAM is in the form of chips, or memory modules, that fit into memory slots on the motherboard. RAM that is not compatible with your system will not load or will not function properly.
Motherboards on modern computers support DDR4 RAM. DDR4 should not be confused with DDR3, the previous generation of SDRAM. They are not interchangeable, and you cannot replace (for example) 8 GB DDR3 with 16 GB DDR4.
DDR4 and SDRAM
Computers use a type of RAM called SDRAM (Synchronous Dynamic Random Access Memory). “Synchronous” DRAM is adjusted according to the processor frequency. SDRAM improves over time, offering advantages such as lower power usage, faster transfer rates, and more stable data transmission.
DDR4 SDRAM is the current standard for modern computers. DDR4 stands for “Double Data Rate 4”, and is the fourth generation of DDR technology, replacing SDR (Single Data Rate) SDRAM. DDR4 has faster data transfer rates, larger capacities, and lower voltages than the previous generation. .
If you’re building a new PC or upgrading RAM in a relatively new system, you’ll probably be using the current standard of DDR4 SDRAM.
Why is DDR4 not backward compatible? Because DDR4 has different timings (see below), voltages, and number of pins, among other characteristics. To prevent accidental installation, the main notch on DDR4 modules is located on different pins than DDR3 modules, which ensures DDR4 cannot be inserted into DDR3 slots.
There are several easy ways to find compatible memory. Check the documentation for your system or processor, run a system profiling utility, or use an online memory compatibility tool.
Shape and Size
DIMM (Dual in-line memory module) is a larger RAM module, designed for desktop motherboards.

SO-DIMM (small outline dual in-line memory module) is a smaller module built for laptops, Intel® NUC mini PCs, and some Mini-ITX small form factor (SFF) motherboards.

Important RAM Specifications
- Capacity : Measured in gigabytes (GB). The higher the capacity, the more data the application can store. At higher capacities, more applications can run simultaneously, and games can store a larger amount of temporary data.
- Speed : Measured in megatransfers per second (MT/s), also often treated as speed in megahertz (MHz), although this is a different measurement than clock speed. Higher speed ratings mean faster responses to read and write requests, leading to improved performance.
How Much RAM Do I Need to Play Games?
Depends. Do you plan on gaming in focused sessions, or do you stream and multitask?
For gaming, 8 GB is considered the minimum standard for AAA titles. However, RAM demands are increasing. Red Dead Redemption 2, for example, recommends 12GB of RAM for optimal performance, while Half-Life: Alyx requires 12GB as a minimum. So, if you want enough space to still be able to play new releases in the future, 16 GB of RAM is recommended.
If you plan to do more than just play games, consider 32 GB. This gives you the freedom to live stream, group chat on Discord, and leave YouTube or Twitch running in the background. If you interested in android gaming, maybe you need to read this article best emulator for 4gb ram pc.
If you’re on a budget and need more RAM (for 3D modeling or other professional applications), Windows 10 Home and the latest Intel® Core™ i9 processor support up to 128 GB. Check “Max Memory Size” under your processor’s memory specifications .
How Much RAM Speed Do I Need?
Find the right balance between capacity and speed. Possibly 32 GB of slow RAM is not an ideal choice, nor is 4 GB of fast RAM.
DDR4 RAM speeds start at around 1600MHz, but this speed is considered slow by today’s standards. The Intel® Core™ i9-10900 processor, for example, supports 2933 MHz according to stock specifications.
For gaming, there is the advantage of running RAM at a high rate of speed. While it won’t have as noticeable an effect as boosting the processor or graphics card, faster RAM can increase the performance and frame rate of games.
Performance boosts differ between games: some get a noticeable improvement, while others have little impact. It would be useful to benchmark against frames per second to see if the increase is worth it.
In addition to increasing frame rates, faster RAM can increase frame time, or frame rate stability. These will be represented as 1% and 0.1% low values (the average of the 1% and lowest 0.1% of recorded frames) in the benchmark.
In addition to frame rates, faster RAM can also improve other areas of system performance, such as speeding up boot times.
Other Considerations
Installation
RAM is usually purchased in two or four module sets (for example, “2×16 GB” or “4×8 GB”). Before buying a kit, check how many memory slots your motherboard has.
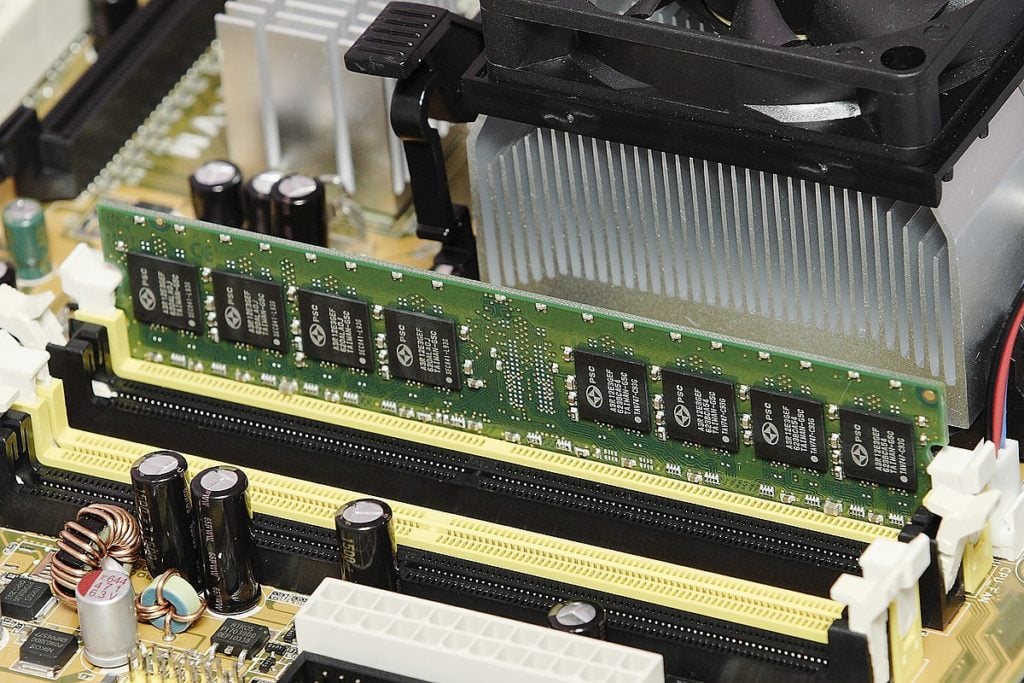
Desktops usually have four slots, while laptops usually have two. Enthusiast-grade PCs and workstations may have eight or more slots, while the number of slots in unique settings such as NUC and SFF will vary.
If you’re planning on upgrading the RAM in your laptop, make sure it’s accessible and not plugged into the motherboard. Some laptop RAM RAM is not meant to be swapped.
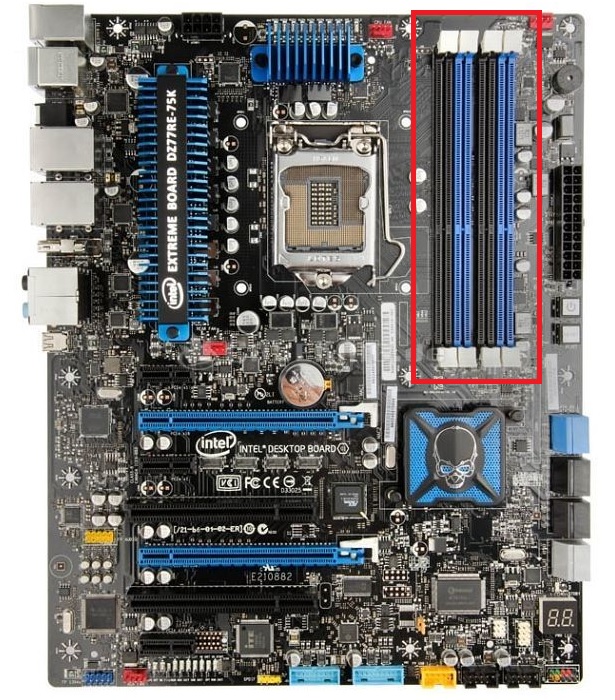

If you plan to upgrade your desktop, try to leave the memory slots open for future expansion whenever possible. For example, installing a 2×16 GB kit instead of a 4×8 GB kit on a desktop leaves you two slots open for future upgrades.
To take advantage of the increased bandwidth provided by dual-channel RAM, it is recommended to install at least a pair of RAM modules in symmetrical slots (usually marked in color). The modules should have the same capacity, and ideally have the same speed: if the speeds don’t match, the slower speed module will be the speed reference.
What is Dual Channel RAM?
Many modern computers are equipped with dual-channel memory. Two-channel mode (inserted or interleaved) allows the CPU memory controller to exchange data with RAM over two channels, reading and writing to two memory chips simultaneously. This increases the available bandwidth.

Two-channel mode is automatically enabled on most motherboards with only two DIMM slots. When using two chips on a motherboard with four slots, however, the memory must be installed symmetrically to use the same channel. Slots are often marked by color, but may also be separate or next to each other. Check the motherboard documentation for more specific instructions.
For ideal performance, ensure that each memory chip has the same speed, capacity, and timing. Avoid mixing and matching modules of different specifications whenever possible.
Memory Timing
RAM speed isn’t the only way to judge performance.
RAM timing is a measurement of latency, or the delay before RAM can execute a given command. The memory timings are given as a series of numbers, such as 16-18-18-36, which may appear on the factory sticker of the module.
Each number corresponds to a specific test. The first number, for example, is Column Address Strobe (CAS) Latency —the number of clock cycles it takes for a memory module to return a set of data after a request from the memory controller.
Comparing RAM modules by timing can be tricky. For example, CAS Latency simply represents the total number of cycles; while the duration of each cycle is also important when assessing responsiveness. For example, DDR3 memory typically has lower CAS Latency than DDR4, but has more labor-intensive performance due to slower clock speeds.
Memory timing is usually not a high priority consideration for gaming PCs. Timings are more attractive to overclockers, who can manually lower the timings in the BIOS, then test stability. If successful, you can get better performance from the existing RAM.
For most gaming PC users, RAM capacity and speed are the most important considerations.
Overclocking RAM
If you’ve purchased high-performance RAM, overclocking can help you achieve more than stock specs. The easiest way to do this is with the Intel® Extreme Memory Profile (Intel® XMP).
When an Intel® XMP profile is selected in the BIOS of a supported motherboard, it adjusts the voltage, timing, and frequency to improve performance. These predefined settings have been tested and certified for stability.
It is also possible to modify the memory profile on some motherboards, as well as manually adjust the settings from the BIOS.
Aesthetics and Cooling
The memory heatsink can make your PC configuration look more attractive. However, they are often just purely aesthetic.

RAM generates heat like any other component, but it won’t get very hot unless it’s operating at unusually high speeds. Please skip the heatsink if you do n’t take RAM overclocking seriously. However, as with any component, it’s a good idea to make sure your memory is exposed to proper airflow .
Memory modules with RGB lighting can also add an element of customization and can increase the visual appeal of your system. Just make sure that the RGB memory chip you choose is compatible with your specific motherboard brand.
What’s the Right Type of RAM for Your Gaming PC?
Finally, how much RAM you need for gaming can depend on your budget and usage plans. Before making a purchase, make sure the RAM specifications match your unique needs.
It is important to balance RAM with the other components of your system, as they will all play a role in determining the overall performance level.
